India & World UpdatesHappeningsBreaking News
Monkeypox: Govt issues guidelines to states/UT’s on disease management
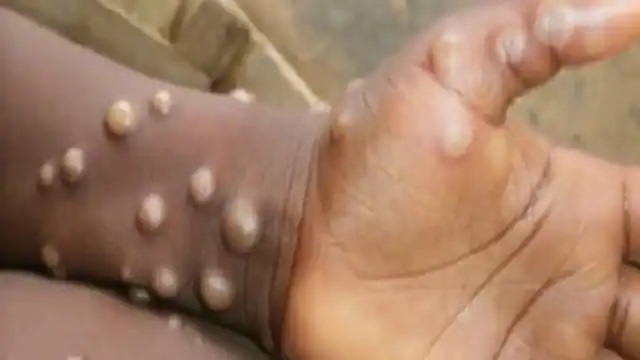
May 31: The Union Health Ministry has issued guidelines to states and Union Territories (UT’s) to manage Monkeypox in view of its spread in non-endemic nations. It listed Monkeypox symptoms- swollen lymph nodes, fever, headache, body aches and profound weakness. Anyone showing one or more of these symptoms with an unexplained acute rash and travel history to an affected country is a suspected case, stated the advisory.
 What are the symptoms of Monkeypox?
What are the symptoms of Monkeypox?
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Rashes
- Fever
- Weakness
- Body ache
- Headaches
- Genital or oral ulcers
- Dehydration
- Nausea
- Conjunctivitis

Once tested positive and a patient goes into isolation, the following symptoms need to be monitored carefully:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Altered consciousness
- Seizures
- Pain in the eye
- Blurred vision
- Poor oral intake
- Lethargy
- Difficulty in breathing
 What are the preventive measures for monkeypox virus?
What are the preventive measures for monkeypox virus?
The Union Health Ministry listed some preventive measures for monkeypox management.
- Avoid contact with any materials, such as the bedding of an infected or sick person
- Isolate infected patients from others
- Practice good hand hygiene after contact with infected animals or humans
- Washing your hands with soap and water or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when caring for patients
What are the risk factors for monkeypox virus?
Health workers and family members of a patient with monkeypox virus are considered high-risk groups for positive patients. Those who are handling the specimens or offering care to suspected or confirmed patients must follow standard infection control measures.
- Precautions to be taken around monkeypox patients
- Patients must be managed well in isolation and one must take all precautions to minimise exposure to the suspected or confirmed patient.
- Place a surgical mask on the nose and mouth of the patient
- Cover the patient’s exposed skin lesions with a gown or sheet properly.





